
The nature of ARC differs from that of Audio Extractors, each providing unique advantages in various scenarios. This article will delve into the technology behind HDMI ARC and outline the distinctions between ARC and eARC. Additionally, it will offer practical tips for utilizing ARC audio and present an overview of other prevalent home audio interfaces.
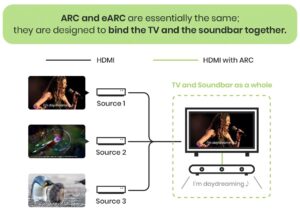
What is HDMI ARC?
HDMI ARC, or Audio Return Channel, was introduced with HDMI version 1.4. It enables audio to travel from a TV back to an audio receiver or soundbar via a single HDMI cable, thus removing the need for a separate audio cable. For example, when using a TV application such as Netflix, ARC allows the audio from the TV to be sent directly to the sound system through the HDMI cable, enhancing sound quality.
What is HDMI eARC?
HDMI eARC, or Enhanced Audio Return Channel, is a more advanced iteration of ARC introduced with HDMI 2.1. eARC provides greater bandwidth and speed, allowing for support of superior audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio, as well as higher-resolution audio. It also offers features like automatic detection of audio systems and better management of audio synchronization, ensuring not only improved sound quality but also more accurate audio-video timing.
ARC vs. eARC: Supported Features
ARC and eARC have several distinguishing features. For queries such as “Do all HDMI cables support ARC?” refer to the table below.
| Feature | ARC | eARC |
| HDMI Version | HDMI 1.4 | HDMI 2.1 |
| Audio Formats | Supports basic compressed audio formats (PCM, Dolby Digital, DTS 5.1) |
Supports higher-resolution, uncompressed audio formats (Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio) |
| Audio Bandwidth | 1.441 Mbps | 37.1 Mbps |
| Audio Delay (Lip Sync) | May have a significant delay | Significantly reduced delay, improved audio-video synchronization |
| Device Compatibility | Manual setup required, possible compatibility issues | Automatic detection and configuration |
| CEC | Supported | Supports a wider range of devices and control functions |
| Cable | Standard HDMI cable | High-quality HDMI cable (e.g., HDMI High Speed with Ethernet) |
Tips for Using ARC/eARC
Not all televisions come with HDMI ARC capability. To identify if a TV has HDMI ARC, one should check for ports labeled “ARC” or “eARC,” which indicate the ability to connect to external audio devices.


To utilize ARC, it may be necessary to activate the ARC feature in the settings of both your television and receiver. The process for enabling ARC can differ across devices; consult the device’s manual or specifications for guidance. Should you experience audio problems, consider using a superior HDMI cable or reactivating the ARC feature. For older equipment, employing ARC or an HDMI audio extractor, such as the QNEX HS42M-4K6G, might be advisable.
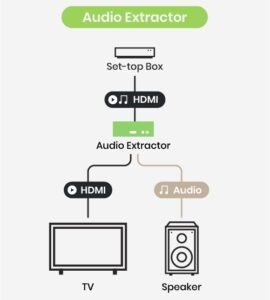
Other Common Home Audio Interfaces
In addition to ARC/eARC, various other audio transmission technologies are prevalent in home audio systems.
SPDIF
The SPDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format) is a digital audio interface co-developed by Sony and Philips. It is capable of transmitting two channels of uncompressed PCM audio or compressed 5.1/7.1 surround sound. For transmission, SPDIF may utilize either optical fiber or coaxial cables.
Similar to eARC, SPDIF maintains the original audio fidelity. Should your TV feature an SPDIF output, connecting it to an amplifier is possible.

TOSLINK
TOSLINK (Toshiba Link) is an optical transmission technology that adheres to the SPDIF standard and was developed by Toshiba. It is capable of transmitting two channels of uncompressed PCM audio or compressed 5.1/7.1 surround sound.
In contrast to SPDIF, TOSLINK exclusively utilizes optical fiber cables, which offer superior resistance to interference and allow for greater transmission distances.

Wireless Transmission
Wireless transmission is advantageous when you need to play audio through an amplifier without connecting to a TV display.
The AV market offers a variety of Bluetooth audio receivers. You can connect one of these receivers to your amplifier, enabling it to receive audio via Bluetooth and transmit it to your speakers. Additionally, Apple’s AirPlay technology is becoming more prevalent in smart TVs and amplifiers, providing superior uncompressed audio quality in comparison to Bluetooth.
Conclusion
In summary, grasping the disparities between HDMI ARC and eARC offers clarity on how each operates within audio-video systems. This knowledge enables users to optimize their setups for seamless audio transmission and enhanced entertainment experiences.
